Biology Chapter 12 Entry test MCQs
Topic 12
Cartilage and Bones
1. It is not a true statement about bones and cartilages:
a. Both contains living cells
b. Both contain various types of living cells
c. Both have ground matrix of collagen
d. Both are part of endoskeleton
2. Which type of cartilage is/are present in our respiratory passage?
a. Fibro cartilage
b. Elastic cartilage
c. Hyaline cartilage
d. All A, B, C
3. All of the following are true about collagen except:
a. Living
b. Inelastic
c. Protein
d. Flexible
4. Cartilage is covered by:
a. Perimysium
b. Periosteum
c. Perineurium
d. Pericondrium
5. Major protein of connective tissues:
a. Titin
b. Collagen
c. Albumin
d. Actin
Divisions of Human Skeleton
6. Tibia is found in:
a. Face
b. Skull
c. Upper arm
d. Lower leg
7. Number of bones present in vertebral column:
a. 33
b. 24
c. 35
d. 26
8. It is not part of axial skeleton:
a. Inferior Choncha
b. Sternum
c. Patella
d. Atlas and axis
9. Ribs which are only attached to spinal cord are:
a. Floating ribs
b. True ribs
c. Costal arch
d. False ribs
10. Choose an option containing correct information:
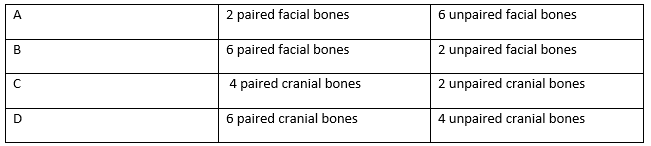
11. How many coxal bones are present in human body?
a. 2
b. 3
c. 4
d. 6
Types of Joints
12. Knee and elbow joints are examples of:
a. Hinge joint
b. Ball and socket joint
c. Fibrous joint
d. Cartilaginous joint
13. Which of the following is an example of synovial joint?
a. Joint between rib and vertebral column
b. Joint between clavicle and scapula
c. Joints between skull bones
d. Joint between radius and ulna
14. Elbow joint is an example of:
a. Hinge joint
b. Ball and socket joint
c. Pivot joint
d. Fibrous joint
15. Joint that is immoveable:
a. Ball and Socket
b. Sutures
c. Pubic symphysis
d. Saddle
16. Joint between costal arch and sternum is:
a. Ball and Socket
b. Fibrous
c. Synovial
d. Cartilaginous
Disorders of Human Skeleton (Gout and Arthritis)
17. Acute forms of arthritis usually results from———-invasion.
a. Bacterial
b. Viral
c. Bacteriophage
d. Fungal
18. Antibodies attack joints in:
a. Gouty arthritis
b. Osteoarthritis
c. Rheumatoid arthritis
d. Juvenile arthritis
Comparison of Muscle Types
19. Irregular striations and involuntary control is related to:
a. Skeletal muscle cells
b. Smooth muscle cells
c. Fibroelastic cartilage cells
d. Cardiac muscle cells
20. Which one of the following is correct regarding ligaments and tendons?
a. Both are inelastic fibrils
b. Both are specialized connective tissue
c. Both are elastic
d. Both form joint capsule
21. Earliest form of muscles is:
a. Smooth
b. Cardiac
c. Striated
d. Skeletal
22. Brachioradialis:
a. Is inserted into radius
b. Originates from radius
c. Is inserted into ulna
d. Originates from ulna
23. The main functional partners of bones are:
a. Skeletal muscle
b. Tendon
c. Nerves
d. Ligament
24. The type of muscle which exhibits striations at regular intervals, is multinucleated and whose control is neurogenic (controlled by the nervous system) is the:
a. Skeletal muscle
b. Smooth muscle
c. Involuntary muscle
d. Cardiac muscle
25. Which one of the following muscles are considered as “Voluntary muscles”?
a. Cardiac muscles
b. Smooth muscles
c. Glandular muscles
d. Skeletal muscles

outstanding and quality mcqs… Really appreciated