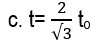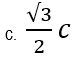12th class (Fsc) Physics unit 8 MCQs
51. A positron is an-anti particle of:
a. Neutron
b. Proton
c. Photon
d. Electron
52. According to Stefan’s Law about black body radiations is:
a. E ∝ T4
b. E ∝ 1/T2
c. E ∝ T
d. E ∝ T2
53. Joule-second is the unit of:
a. Plank’s constant
b. Energy
c. Boyle’s law
d. Wien’s constant
54. Antiparticle of electron is:
a. Neutron
b. Proton
c. Positron
d. Photon
55. The existence of position is 1928 was predicted by:
a. Chadwick
b. Anderson
c. Plank
d. Dirac
56. The value of Plant’s constant h is:
a. 6.63×10-34js-2
b. 6.63×10-34js
c. 6.63×10-34j/s-2
d. 6.63×10-34j/s
57. Rest mass of photon is:
a. 931 MeV
b. 1.02 MeV
c. 200 MeV
d. 0.51 MeV
58. When the K.Emax of photoelectron is zero, the frequency of incident photon is:
a. Much than
b. Less than
c. Equal to
d. Greater than
59. In annihilation, emitted photons move in opposite directions to conserve.
a. Energy
b. Mass
c. Momentum
d. Charge
60. Wave nature of light appears in:
a. Photo electric
b. Pair production
c. Interference
d. Compton effect
61. The Compton shift is equal to Compton wavelength at an angle of:
a. 45o
b. Zero
c. 90o
d. 120o
62. Which is the most refined form of matter?
a. Light
b. Smoke
c. Electron
d. Fog
63. If a particle of mass “m” is moving with speed “v” then de-Broglie wavelength λ associated with it will be:
a. λ= h/mv
b. λ= 3h/mv
c. λ= h/2mv
d. λ= 2h/mv
64.The energy of photon is given by:
a. voe
b. mv2/2
c. moc2
d. Hf
65. The principle regarding the dual nature of light was first discovered by:
a. Electron microscope
b. Photodiode
c. Compound microscope
d. Optical microscope
66. Application of wave like nature of particle is:
a. Electron microscope
b. Photodiode
c. Compound microscope
d. Optical microscope
67. Pair production can take place only when energy of radiation is equal and greater than 1.02 MeV, thus correct option is:
a. Y-rays
b. X-rays
c. Ultraviolet rays
d. Heat Radiation
68. Inertial frame is a frame in which:
a. 3rd law hold
b. 1st law holds
c. Kelvin’s law holds
d. 2nd law holds
69. Two oppositely charged balls A and B attract the third ball C, when placed near them turn by turn. The third ball C must be:
a. Electrically neutral
b. Positively charged
c. Positively and negatively charged
d. Negatively charged
70. The wavelength associated with the proton moving at a speed of 40 m/s is:
a. 15.7 nm
b. 7.20 nm
c. 17.3 nm
d. 9.02 nm
71. The energy of the photon of wavelength 500 nm is:
a. 1.77 eV
b. 3.10 eV
c. 1.52 eV
d. 2.49 eV
72. The photon with energy greater than 1.02 MeV can interact with matter as:
a. Pair production
b. Photoelectric effect
c. Annihilation of matter
d. Compton effect
73. By modern system of NAVSTAR, the speed anywhere on the earth can be determined to accuracy about:
a. 2 cms-1
b. 20 ms-1
c. 2 ms-1
d. 10 ms-1
74. Which one is low energy photon?
a. Ultra violet light
b. Visible light
c. X-rays
d. Infrared light
75. The unit of Plan’s constant is:
a. Watt
b. Joule
c. Candela
d. Joule-s
76. When speed of object is half of the speed of light, then:
a. t= 3to / √2
b. t= to
![]()
d. t= 2to
77. For what speed of an object, its relativistic time is double of the proper time?
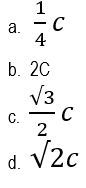
78. Light of 4.5eV is incident on a cesium surface and stopping potential is 0.25V, maximum K.E of emitted electrons is:
a. 4.75 eV
b. 4.5 eV
c. 0.25 eV
d. 4.25 eV
79. The materialization of energy takes place in the process of:
a. Pair production
b. Photoelectric effect
c. Annihilation of matter
d. Compton effect
80. Assuming you radiate as does a black body at your body temperature about 37o C then the radiated max wave length in λ m is:
a. 10μm
b. 11.6μm
c. 10.93μm
d. 9.35μm
81. The momentum of photon of frequency ‘f’ is:
a. f/hc
b. hc/f
c. c/hf
d. hf/c
82. Using relativistic effects, the location of an air craft after an hr fight can be predicated about:
a. 760m
b. 20m
c. 780m
d. 50m
83. The momentum of photon is given by the equation:
a. P= λ/h
b. P= mv
c. P= hλ
d. P= h/λ
84. The number of electrons emitted depend upon:
a. Frequency of incident light
b. Color of target surface
c. Intensity of incident light
d. Shape of surface
click here to go directly on chapter no.9