Chemistry Chapter 10 Entry Test MCQs
Topic 10
Chemical Bonding + Radii of atoms
1. Which of the following represents elements in order of increasing atomic size?
a. C, N, O
b. La, Br, Cl
c. Li, Na, K
d. Na, Mg, C
2. Which one of the following triad does not follow octet rule?
a. PCl5, BeCl2, SF3
b. NH3, PH3, BF3
c. BF3, AlCl3, NH3
d. H2O, H2S, H2Te
I.E + E.A + E.N
3. The element which has highest 1st ionization energy:
a. 1s2
b. 1s2 2s2 2p6
c. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
d. 1s2 2s2 2p3
4. The one having highest ionization energy is
a. Al
b. Mg
c. P
d. S
5. Which element would be the least electronegative element with
a. low I.E. and low E.A.
b. high I.E. and low E.A.
c. high I.E. and low E.A
d. low I.E. and high E.A.
6. Electronegativity difference decides nature of bond. If electronegativity difference is greater than 1.7, bond is ionic. Which of the following is ionic compound (electronegativities are, F=4.0, H=2.1, Cl= 3.0, I= 2.5):
a. HCl
b. HF
c. HI
d. None
7. The graph represents the variation of a property of the Group II elements
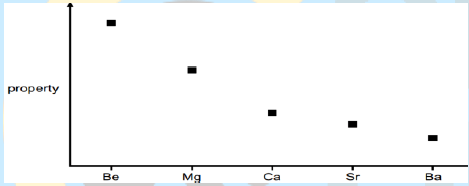
What is this property?
a. Solubility of oxides in water
b. Ionization energy
c. Neutron / proton ratio
d. Rate of reaction with water
8. Identify the correct order in which the ionic radius of the following ions increases:
(I) F– (II) Na+ (III) N3-
a. I, II, III
b. III, I, II
c. II, I, III
d. II, III, I
9. Correct decreasing order of the ionization energy for the following elements is
a. Ne > Cl > S > P > Mg > Al
b. Ne > Cl > P > S > Al > Mg
c. Ne > Cl > S > P > Al > Mg
d. Ne > Cl > P > S > Al > Mg
10. Identify the wrong statement in the following
a. Amongst isoelectronic species, smaller the positive charge on cation, smaller is the ionic radius
b. Atomic radius of the elements increases down the first group of the periodic table
c. Amongst isoelectronic species, greater the negative charge on the anion, larger is the ionic radius
d. Atomic radius of the elements decreases across from left to right in 2nd period of the periodic table
11. Which one of the following sets of ions represents a collection of isoelectronic species?
a. N3–, O2–, S2–
b. K+, Ca2+, Sc3+
c. Li+, Na+, Mg2+
d. Ba2+, K+, S2–
12. Electronic configuration of different elements is given. Which has highest 1st ionization energy?
a. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
b. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p1
c. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2
d. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5
Bond Types
13. The % age ionic character in a covalent molecule can be find out by the formula:
a. μtheoretical/μexperimental × 100
b. μobserved/μionic × 100
c. μionic/μcovalent × 100
d. μexperimental/μtheoretical × 100
14. The elements whose electro negativities are 1.2 and 3.0 react to form:
a. liquid substance
b. ionic bond
c. gaseous substance
d. covalent bond
15. Indicate the nature of bonding in both CH4 & NaH:
a. covalent in CH4 & electrovalent in NaH
b. covalent in both
c. electrovalent in CH4 & covalent in NaH
d. ionic in both
16. In a crystal, the cations & anions are held together by:
a. electrostatic force
b. sharing of electrons
c. Electrons
d. Nuclear forces
17. Which of the following has non directional bond?
a. KBr
b. BF3
c. NF3
d. H2O
18. Indicate which of the following forms multiple bond:
a. C2H5OH
b. CH3CN
c. CH4
d. C3H8
19. Which of the following has coordinate covalent and ionic bond?
a. HCl
b. NaCl
c. AlCl3
d. NH4Cl
20. Which of the following is electron deficient molecule?
a. B2H6
b. PH3
c. PCl5
d. SiH4
21. The types of bonds present in CuSO4.5H2O are only:
a. covalent and coordinate covalent
b. electrovalent and covalent
c. electrovalent and coordinate covalent
d. covalent and coordinate covalent
23. Which one of the following does not have dative covalent Bond?
a. HClO
b. HClO4
c. HClO2
d. HClO3
24. The type(s) of bonding present in a sample of sodium nitrated, NaNO3, are:
a. Ionic and metallic bonds
b. Covalent bonds only
c. Covalent and ionic bonds and coordinate covalent
d. Ionic bonds only
25. Electronegativity difference makes molecules polar and they have certain value of dipole moment. Among following which is not polar molecule
a. SF6
b. XeF2
c. CO
d. ClO2
