Chemistry Chapter 10 Entry Test MCQs
51. dsp3 hybridization of central atom is present in one of the following compounds:
a. CHCl3
b. NF3
c. PCl5
d. BF3
52. Hybridization of 1 and 2 carbon atom in CH2=C=CH2 are respectively:
a. sp3, sp2
b. sp, sp
c. sp, sp2
d. sp2, sp
53. –Which of the following is not incorrect statement?
a. π-bonds and σ-bonds involve in hybridization
b. It explains trivalent nature of carbon
c. Hybridization explains paramagnetic behaviour of oxygen
d. All are incorrect
54. Linear overlapping results in σ-bond formation and parallel overlapping forms π-bond. Among the following, which always form π-bond
a. pz-pz
b. s-s
c. s-p
d. none
55. Which of the following molecules has the smallest bond angle?
a. H2S
b. NH3
c. H2Se
d. H2O
56. d2sp3 hybridization of atomic orbital’s gives:
a. Square planar structure
b. Triangular structure.
c. Octahedral structure.
d. Tetragonal structure
57. The bond angle and dipole moment of water, respectively are
a. 104.5o, 1.84 D
b. 102.5o, 1.56 D
c. 109.5o 1.84 D
d. 107.5o, 1.56 D
58. The angular shape of ozone molecule (O3) consist of:
a. 2 sigma and 1 pi bonds.
b. 1 sigma and 1 pi bonds.
c. 2 sigma and 2 pi bonds.
d. 1 sigma and 2 pi bonds.
59. The hybridization of oxygen atom in H2O2 is:
a. sp2
b. sp3
c. sp3d2
d. sp
60. The correct sequence of increasing covalent character is represented by
a. NaCl < LiCl < BeCl2
b. LiCl < NaCl < BeCl2
c. BeCl2 < NaCl < LiCl
d. BeCl2 < LiCl < NaCl
61. Bond angle of 109°28’ is found in
a. CH3+
b. NH3
c. NH4+
d. H2O
62. Which molecule has smallest bond angle?
a. H2S
b. SO2
c. NH3
d. H2O
63. Which type of the orbital hybridization and geometry is used by the central atom of NH2 –?
a. sp hybridization and tetrahedral geometry
b. sp2 hybridization and trigonal planar
c. sp3 hybridization and tetrahedral geometry
d. sp2 hybridization and trigonal planar
64. Identify the compound below which has bonds formed by an overlap of sp and p–orbitals
a. NH3
b. BF3
c. H2O
d. BeCl2
65. When ammonia molecule donates pair of electron to H+ to form NH4+ ion then the angles.
a. Increases upto 1200
b. Increases upto 109.50
c. Increases upto 1800
d. Decreases upto 109.50
66. CCl4 has no dipole moment because of:
a. Similar size of C and Cl
b. Regular tetrahedral structure
c. Its planner structure
d. Similar electron affinities of C and Cl
67. Which of the following statements is correct?
a. BF3 involves sp3 hybridization and NF3 involves sp2 hybridization
b. BF3 involves sp2 hybridization and NF3 involves sp3 hybridization
c. Both BF3 and NF3 involve sp3 hybridization
d. Both BF3 and NF3 involve sp2 hybridization
68. Which set of hybridization states of C1, C2, and C3 of the following molecule is correct?
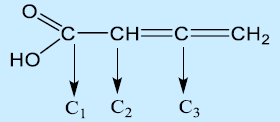
a. sp2, sp2, sp2
b. sp2, sp2, sp
c. sp3, sp2, sp
d. sp3, sp2, sp2
69. Which of the following set contains species having same angle around the central atom?
a. BF3 , NF3 , AlCl3
b. SF4 , CH4 , SeF4
c. BF3 , BCl3 , BBr3
d. NF3 , BCl3 , NH3
70. The correct order of bond angles (smallest first) in H2S, NH3, BF3 and SiH4 is:
a. H2S < NH3 < SiH4 < BF3
b. H2S < SiH4 < NH3 < BF3
c. H2S < NH3 < BF3 < SiH4
d. NH3 < H2S < SiH4 < BF3
71. Bond angle of NH3 , PH3 , AsH3 , and SbH3 is in the order
a. PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3 > NH3
b. SbH3 > AsH3 > PH3 > NH3
c. NH3 > PH3 > AsH3 > SbH3
d. SbH3 > AsH3 > NH3 > PH3
72. Identify the triade in which all the species have same geometry.
a. NH3, CH3+, H3O+
b. NO2, SO2, CO2
c. CH3+, BF3, NH3
d. NO3-1, CH3+, CO3-2
73. The hybridisation of atomic orbitals of nitrogen in NO2+, NO3– and NH4+ are
a. sp, sp2 and sp3 respectively
b. sp, sp3 and sp2 respectively
c. sp2, sp3 and sp respectively
d. sp2, sp and sp3 respectively
74. Which one of the following statements about orbital hybridization is incorrect?
a. The carbon atom in CO2 is sp2 hybridized
b. The nitrogen atom in NH3 is sp3 hybridized
c. sp hybrid orbitals lie at 180o to each other
d. sp2 hybrid orbitals are coplanar, and at 120o to each other.
75. Which is correct about carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide?
a. Both are polar
b. Both have sp-hybridized carbon
c. Both are acidic
d. Both contain four lone pairs
