Chemistry Chapter 13 Entry Test MCQs
26. Which term is used to convert higher alkane into lower alkane / alkene
a. Catalysis
b. Pyrolysis
c. Electrolysis
d. Hydrolysis
27. Which of the following is excellent anti knock agent?
a. (C2H5)4Pb
b. Al2O3
c. AlCl3
d. SiO2
28. As the number of carbon atoms in the homologous series of alkanes increase numerical value the following property decrease:
a. Enthalpy of vaporization
b. Number of isomers
c. Vapour pressure
d. Density
29. Process in which coal is heated in the absence of air at high temperature and converted into coal gas, coal tar, and coke is called
a. burning of coal
b. destructive distillation
c. burning of oxygen
d. distillation
30. Which is not a product of destructive distillation of coal:
a. Coal tar
b. Coke
c. Ligroin
d. Coal gas
31. The formula of an organic compound having cyclic structure and unsaturated is
a. C6H6Cl6
b. C6H12
c. C6H10
d. C5H12
32. The petrol having octane number 80 has
a. 80% normal heptane + 20% iso-octane
b. 20% normal heptane + 80% iso-octane
c. 80% normal heptane + 20% normal octane
d. 20% normal heptane + 80% normal octane
33. In the commercial gasolines, the type of hydrocarbons which are more desirable is
a. Straight-chain hydrocarbon
b. Branched hydrocarbon
c. Toluene
d. Linear unsaturated hydrocarbon
34. Petroleum consists mainly of
a. Aliphatic alcohols
b. Aliphatic hydrocarbons
c. Phenols
d. Aromatic hydrocarbons
35. When ethyl iodide and propyl iodide react with Na in the presence of ether, they form
a. Four alkanes
b. One alkane
c. Three alkanes
d. Two alkanes
36. Paraffin wax is
a. Saturated hydrocarbons
b. Unsaturated hydrocarbon
c. Alcohol
d. Ester
Functional Groups
37. Esters can be presented by:
a. R-CO-R
b. R-OH
c. R-O-R
d. R-COOR
38. All the following compounds have benzene ring in their fused form except:
a. Naphthalene
b. Phenanthrene
c. Anthracene
d. Diphenylmethane
39. Urea has the main functional group:
a. Ether
b. Amine
c. Acid amide
d. Carboxylic acid
40. Alkanone is another name of:
a. Aldehydes
b. Carboxylic acids
c. Ketones
d. Alcohols
41. The general formulas CnH2nO2 could be for open chain
a. Diols
b. Diketones
c. Dialdehydes
d. Carboxylic acids
42. Which of the following compound is bifunctional:
a. Acetone
b. Salicylic acid
c. Methanol
d. Alkyl halide
43. Which one of the following acid do not contain carboxylic group?
a. Carbolic acid
b. Phthalic acid
c. Salicyclic acid
d. All contain
44. Urea has the functional group:
a. Ether
b. Imine
c. Acid amide
d. Carboxylic acid
45. The general formula (RCO)2O represents:
a. An acid anhydride
b. An ester
c. An aldehyde
d. An ether
46. Name an organic compound in which RCOOCOR is a functional group?
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Ester
c. Dimethyl ether
d. Acid anhydride
47. Which of the following compound has the functional group –COH
a. Nitrobenzene
b. 1, 2-ethandiol
c. Ethanal
d. 2-butanone
48. How many functional groups are present in its formula?
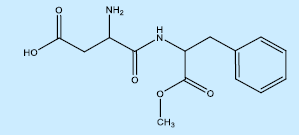
a. 1
b. 3
c. 4
d. 2
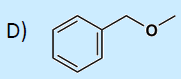
49. Which compound is not an ether?
a. CH3CH2OCH2CH3
b. CH3COCH2CH3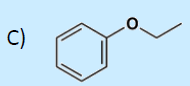
50. As the priority of functional group is improved, the oxidation state of carbon:
a. Remains constant
b. Increase
c. Becomes zero
d. Decrease
