Chemistry Chapter 13 Entry Test MCQs
Hybridization
51. The bond present in ethylene are:
a. 1 sigma and 1 pi bond
b. 3 sigma and 3 pi bond
c. 1 pi and 5 sigma bond
d. 1 pi and 3 sigma bond
52. Carbon atom HCN is:
a. Sp3 hybridized
b. sp hybridized
c. Not hybridized
d. sp2 hybridized
53. The bond present in acetylene are:
a. 1 σ and 1 π bond
b. 3 σ and 3 π bond
c. 1 π and 5 σ bond
d. 2 π and 3 σ bond
54. Carbon atom of HCHO (methanal, formaldehyde) is:
a. Sp3 hybridized
b. sp hybridized
c. Not hybridized
d. sp2 hybridized
55. Which of the following orders regarding the size of hybrid orbital of carbon is correct?
a. sp > sp2 < sp3
b. sp > sp2 > sp3
c. sp < sp2 > sp3
d. sp < sp2 < sp3
56. Which of following orders regarding the electronegativity of hybrid orbital of carbon is correct?
a. sp > sp2 < sp3
b. sp > sp2 > sp3
c. sp < sp2 > sp3
d. sp < sp2 < sp3
Isomerism
57. Isomerism in saturated hydrocarbons is due to
a. Change in the valence of carbon
b. Change in the ratio of elements in compounds
c. Formation of double bond
d. Formation of branches in the chain of C atoms
58. How many esters are there with the molecular C4H8O2?
a. 4
b. 2
c. 6
d. 3
59. Consider the following organic compound,
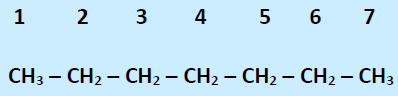
To make it a chiral compound, the mono-substituition of nucleophile should be on carbon
a. 1
b. 4
c. 3
d. 7
60. Ortho-xylene and para-xylene are the example of:
a. Position isomerism
b. Metamerism
c. Tautomerism
d. Chain isomerism
61. What type of isomerism is shown by n-pentane, iso-pentane and neo-pentane?
a. Geometric isomerism
b. Position isomerism
c. Chain isomerism
d. Metamerism
62. Diethyl ketone and methyl – n – propyl ketone are isomers of each other?
a. Functional group
b. Tautomers
c. Metamersim
d. Geometric
63. Geometrical isomerism is possible in:
a. H3CHC = C(CH3)2
b. ClHC = CCl2
c. H3CHC = CClBr
d. H3CHC = CH2
64. The number of isomers of C6H14 is:
a. 6
b. 4
c. 7
d. 5
65. All of the following show keto-enol tautomerism EXCEPT:
a. C6H5 – CO – C6H5
b. C6H5–CO–CH2Cl
c. H – CO – CH3
d. C6H5–CO– CHCl2
66. The compound which is not isomeric with diethyl ether:
a. 2-methyl-2-propanol
b. n-propyl-methyl ether
c. 2-butanone
d. 1-butanol
67. These are geometrical isomers:
a. Maleic acid and fumaric acid
b. Maleic acid and maleic anhydride
c. Ethylene dichloride and 1, 2-dichloroethene
d. None of these
68. Which is a pair of geometrical isomers?
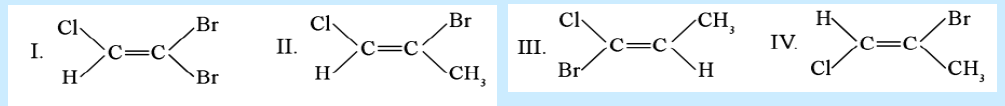
a. I and III
b. II and IV
c. III and IV
d. I and II
69. The number of possible alkynes with molecular formula C5H8 is
a. 5
b. 3
c. 6
d. 4
70. The two optical isomers given below, namely
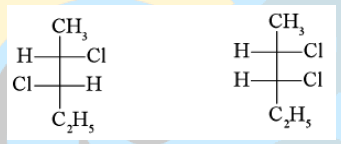
a. Enantiomers
b. Diastereomers
c. Mesomers
d. Structural isomers
71. The number of optical isomers formed by hydrogenation of (CH3)2C CHCH3 are:
a. 2
b. 0
c. 3
d. 1
72. How many cyclic isomers are possible for C5H10.
a. 5
b. 3
c. 6
d. 4
73. Which of the following does not show geometrical isomerism?
a. 1,2-Dichloro-1-pentene
b. 1,1-Dichloro-1-pentene
c. 1,4-Dichloro-1-pentene
d. 1,3-Dichloro-1-pentene
74. An optically active compound is
a. β-Bromobutyric acid
b. 1-Bromobutane
c. 1-Bromo-2-methylpropane
d. 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
75. Methoxy methane is a __ isomer of ethyl alcohol.
a. Functional group
b. Metamer
c. Position isomer
d. Tautomer
