Chemistry Chapter 13 Entry Test MCQs
76. Cholesterol is the most abundant sterol in animals and is present in blood in free and esterified form. It forms blood plaque in arteries causing blood pressure and other heart diseases. Number of chiral centers in side chain of cholesterol are
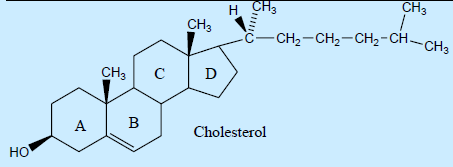
a. zero
b. Two
c. Eight
d. one
77. A racemic mixture is formed by mixing two
a. Geometric isomers
b. Optically Active compounds
c. Structural isomers
d. Meso Compounds
78. Isomers have essentially identical
a. Molecular formula
b. Structural formula
c. Physical properties
d. Chemical properties
79. Number of optical isomers of lactic acid are
a. 3
b. 1
c. 4
d. 2
80. Maximum number of isomers of C4H8 are
a. 4
b. 2
c. 6
d. 3
81. An organic compound exhibits optical isomerism when
a. Two groups linked to carbon atom are different
b. Four groups linked to carbon atom are different
c. All the groups linked to carbon atom are same
d. Three groups linked to carbon atom are different
82. The molecular formula of diphenyl methane is C13H12. How many structural isomers are possible when one of the hydrogen is replaced by a Cl- atom?
a. 4
b. 6
c. 8
d. 9
83. Diastereomers are
a. Isomers that only differ by rotations around single bonds.
b. Stereisomers that are nonsuperimposable non mirror images.
c. Isomers that only differ in the bonding arrangement of the atoms.
d. Stereisomers that are nonsuperimposible mirror images.
84. Which of the following contains asymmetric centre.
a. 2-hexyne
b. 2-butene
c. Lactic acid
d. 2,2-dimethylpropane
85. Which of the following pairs are not isomeric compounds
a. Butanone and butanal
b. Ethyl ethanoate and methyl propanoate
c. Methoxy methane and ethanol
d. Ethoxy propane and propoxy methane
86. Lactic acid in which a methyl group, a hydroxyl group, a carboxylic acid group and a hydrogen atom are attached to a central carbon atom, shown optical isomerism due to the molecular geometry at the
a. Carbon atom of the methyl group
b. Central carbon atom
c. Oxygen of the hydroxyl groups
d. Carbon atom of the carboxylic acid group
87. An organic compound C4H8O, is found to be optically active. Which of the following could it be?
a. CH2 = CH – CH(OH) – CH3
b. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO
c. (CH3) 2 CH – CHO
d. CH2 – CO – CH2 – CH3
88. The number of possible open chain (acyclic) isomeric compounds for molecular formula C5H10 would be:
a. 7
b. 5
c. 8
d. 6
89. Which of the following don’t involve in any type of structural isomerism:
a. Propane
b. Pentane
c. Propene
d. Ethanol
90. How many structural (including stereo isomers) isomers could be obtained by replacing one hydrogen of propene with chlorine?
a. 4
b. 2
c. 5
d. 3
91. Which organic structure among the following is not an isomer of the compound?
CH3 – CO – CH2CH2CH2CH3?
a. CH3CH2OCH = CHCH2CH3
b. CH3CH = CHCH2CH2CHO
c. (CH3)2CH – CO – CH2CH3
d. CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3
92. Which of the following compounds will show metamerism?
a. CH3 – CO – C2H5
b. CH3 – O – C2H5
c. C2H5 – S – C2H5
d. CH3 – O – CH3
93. Glucose and fructose are:
a. Functional group isomers
b. Cis-trans isomers
c. Chain isomers
d. Metamers
94. Cis-trans isomers can be differentiated by:
a. Dipole moment
b. Melting point
c. Boiling point
d. All of these
95. Tautomerism can also to called:
a. Prototropism
b. Chain isomerism
c. Geometrical isomerism
d. Metamerism
96. Which of the following has zero dipole moment?
a. Trans-2-butene
b. 2-methyl-1-propene
c. Cis-2-butene
d. 1-butene
97. How many total isomers are with the molecular C4H8O2?
a. 4
b. 2
c. 6
d. 3
98. Number of isomers represented by molecular formula C4H10O is
a. 4
b. 3
c. 10
d. 7
100. Which of the following is optically active
a. Glycerol
b. Ethylene glycol
c. Tartaric acid
d. Oxalic acid
101. Number of isomeric primary amines obtained from C4H11N are
a. 5
b. 3
c. 6
d. 4
102. The number of enantiomers of the compound CH3CHBrCHBrCOOH is
a. 3
b. 1
c. 4
d. 2
103. Which of the following have asymmetric carbon atoms
- CICH2 – CH2Br 2. CH3 – CHCI2 3. CH3 – CHBrCI 4. CH2Br – CHOH – CH3
a. 1, 2, 3
b. 1, 3, 4
c. 2, 3, 4
d. 3, 4
104. Which isomerism is possible for 2-Chloro-3-methylbutane:
a. Cis-trans isomerism
b. Functional group isomerism
c. Positional isomerism
d. Metamerism
105. Which of the following pair shows functional group isomerism
a. ethanol and methoxy methane
b. n-propyl alcohol and iso-propyl alcohol
c. 1-butene and 2-butene
d. none of the above
