Chemistry Chapter 14 Entry Test MCQs
26. Heterolysis of propane gives:
a. Methyl anion and ethylium cation
b. Methyl and ethyl free radicals
c. Methylium and ethylium cation
d. Methyl cation and ethyl anion
27. The most stable carbonium ion is:
a. (CH3)2C+
b. (C6H5)3C+
c. CH3–CH2+
d. (CH3)3C+
28. Which of the following is not planar?
a. Ter-butyl carbanion
b. Ter-butyl free radical
c. Allyl carbocation
d. Ter-butyl carbocation
29. The most stable carbanion is:
a. (CH3)2CH–
b. CH3–
c. (CH3)3C–
d. CH3CH2–
30. Heterolysis of carbon-chlorine bond produces
a. Two carbonium ions
b. Two free radicals
c. One cation and one anion
d. Two carbanions
31. The reaction intermediate produced by homolytic cleavage of bond is called
a. Free radical
b. Carbanion
c. Carbene
d. Carbocation
Alkanes
32. Which of the following orders regarding the C—H bond distance in CH4, C2H4 and C2H2 is correct?
a. CH4>C2H4<C2H2
b. CH4> C2H4> C2H2
c. CH4C2H2
d. CH4<C2H4<C2H2
33. Which of the following is the major product of the following reaction?
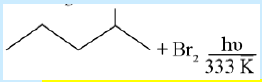
a. 2- bromo -2- methylpentane
b. 1 – bromo – 2- methylpentane
c. 4- bromo -2- methylpentane
d. 3- bromo -2- methylpentane
34. Chlorination of n-butane produces
a. 2-chlorobutane as the chief product
b. 1-chlorobutane as the chief product
c. 2-chlorobutane more than 1-cholorobutane
d. 1-chlorobutane more than 2-chlorobutane
36. Which of the following represent the correct ranking in terms of increasing boiling point?
a. 2-butanone < n-pentane < diethyl ether < 1-butanol
b. n-pentane < diethyl ether < 2-butanone < 1-butanol
c. n-pentane < 2-butanone < diethyl ether < 1-butanol
d. n-pentane < diethyl ether < 1-butanol < 2-butanone
37. Which of the following reaction does not depend upon the concentration of reactants?
a. CH4 with Cl2 in absence of sunlight
b. CH4 with Cl2 in presence of sunlight
c. CH4 with F2 in absence of sunlight
d. CH4 with Br2 in presence of heat
38. Conversion of acetic acid into methane is
a. dehydration
b. Hydration
c. decarboxylation
d. Kolbe’s reaction
39. Formation of an alkane from the reduction of an alkyl halide with Zn is known as
a. Kolbe reaction
b. Cannizzaro reaction
c. Wurtz reaction
d. Frankland reaction
40. When salt of 2-methylpropanoic acid is electrolyzed in aqueous solution, the resultant product obtained,
a. 2,3-dimethylbutane
b. N-hexane
c. n-Butane
d. propane
41. Which of the following has highest percentage of hydrogen?
a. C6H6
b. CH4
c. C2H2
d. C2H4
42. Methane reacts with oxygen at 100 atm. and 300oC in presence of Cu to give
a. Methyl alcohol
b. Acetaldehyde
c. Ethyl alcohol
d. Acetic acid
43. Enthalpy of combustion of methane in kJ mol-1 is:
a. -208
b. -891
c. -240
d. -358.5
44. The decreasing order of boiling points is
a. iso-Pentane > n-Pentane > neo-Pentane
b. n-Pentane > iso-Pentane > neo-Pentane
c. n-Pentane > neo-Pentane > iso-Pentane
d. neo-Pentane > iso-Pentane > n-Pentane
45. The most volatile compound is
a. Isobutane
b. 2, 2-dimethyl propane
c. n-pentane
d. 2-methyl butane
46. Which of the following statements is not true for ethane?
a. It can be catalytically hydrogenated
b. It can be chlorinated with chlorine
c. It is a homologue of iso-propane
d. When oxidised produces CO2 and H2O
47. In the preparation of alkanes; a concentrated aqueous solution of sodium or potassium salts of saturated carboxylic acid are subjected to
a. Hydrogenation
b. Hydrolysis
c. Electrolysis
d. Oxidation
48. The preparation of ethane by electrolysis of aqueous solution of potassium acetate is called as
a. Sabatier-Senderen’s reaction
b. Wurtz reaction
c. Grignard reaction
d. Kolbe’s synthesis
49. Carbon black, which is used in making printer’s ink, is obtained by decomposition of
a. Carbon tetrachloride
b. Acetylene
c. Methane
d. Benzene
50. Which of the following is not linked with methane?
a. Laughing gas
b. Marsh gas
c. Coal gas
d. Natural gas
