Chemistry Chapter 15 Entry Test MCQs
26. During SN2 mechanism carbon atom changes its state of hybridization as
a. sp3→sp
b. sp→sp2
c. sp3→sp2
d. sp2→sp3
27. Which alkyl halide out of the following may follow both SN1 and SN2 mechanism?
a. (CH3)2CH – X
b. CH3-X
c. (CH3)3C – X
d. (CH3)3C-CH2 – X
28. In elimination reactions of alkyl halide which site is more susceptible for the attack of base
a. – oxygen
b. Carbon
c. – hydrogen
d. – chlorine
29. For which mechanisms the first step involved is the same?
a. E1 and SN1
b. E1 + E2
c. SN1 and SN2
d. E2 + SN2
30. Which of the following undergoes nucleophilic substitution exclusively by SN1 mechanism?
a. Chlorobenzene
b. Benzyl Chloride
c. Isopropyl chloride
d. Ethyl chloride
31. C-Cl bond of chlorobenzene in comparison to C-Cl bond in methyl chloride is
a. Shorter and stronger
b. Longer and weaker
c. Longer and stronger
d. Shorter and weaker
32. The alky halide molecule on which the nucleophile attacks is called_______
a. Substrate
b. Electrophile
c. Electrophilic center
d. Leaving group
33. Which of the following is correct about SN2 reactions?
a. 2nd order kinetics
b. Breakage of C—X and formation C—Nu bonds are simultaneous
c. Inversion of the configuration of the alky I halide molecule
d. All of these
34. Primary alkyl halides give:
a. Either E1 or E2 reactions
b. E2 and SN2 reactions
c. SN2 and E1 reactions
d. E1 and SN2 reactions
35. Which statement is incorrect about the reactivity of alky I halides?
a. Great the bond energy of R-X, smaller the stability
b. Great the bond energy of R-X, the lesser the reactivity
c. Great E.N different of R-X greater the stability
d. Great the bond polarity of R-X, the lesser the reactivity
36. Which statement is incorrect about nucleophilic substitution reaction?
a. Tertiary alkyl halides generally give SN1 reactions
b. The incoming nucleophile must be stronger than the leaving one
c. SN2 is a single step mechanism
d. The leaving nucleophile must be stronger than the incoming nucleophile
37. Which pair of reactant gives the ethyl acetate as a product?
a. C2H5Br +2[H]
b. C2H5Br +CH3O
c. C2H5Br +CH3COONa
d. C2H5Br +CN–
38. Among the following alkyl halides, choose the one with the lowest boiling point.
a. t-butyl bromide
b. t-butyl chloride
c. n-butyl iodide
d. n-butyl chloride
39. The reaction of 4-bromobenzyl chloride with NaCN in ethanol leads to:
a. 4-cyanobenzyl cyanide
b. 4-bromo-2-cyanobenzyl chloride
c. 4-bromobenzyl cyanide
d. 4-cyanobenzyl chloride
40. The order of the ease of formation of cabonium ion of alkyl halide is
a. Sec. > Prim. > Tert
b. Prim. > Sec. > Tert
c. Tert > Pri. > Sec.
d. Tert. > Sec. > Prim.
41. 1,2-dibromoethane reacts with alcoholic KOH to yield a product X. The hybridization state of the carbons present in X, respectively are
a. sp3, sp2
b. sp2, sp2
c. sp3, sp3
d. sp, sp
42. The organic chloro compound, which shows complete stereochemical inversion during a SN2 reaction, is
a. (CH3)2CHCI
b. (C2H5)2 CHCI
c. CH3CI
d. (CH3)3CCI
43. For the following: (1) I– (2) CI– (3) Br– the increasing order of nucleophilicity would be
a. I– < Cl– < Br–
b. I– < Br– < Cl–
c. Br– < Cl–< I–
d. Cl– < Br– < I–
44. Which of following undergoes E, elimination in presence of a strong base to yield one product?
a. 1 – bromo -1- methylcyclohexane
b. 3- bromo -2- methylpentane
c. 3- bromo -3- methylpentane
d. 1- bromo -3, 3- dimethylbutane
45. Dehydrobromination of the following is in the order:
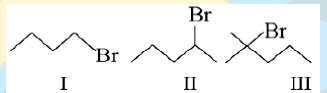
a. III > II > I
b. I > II > III
c. II > III > I
d. II > I > III
46. When bromoethane is heated under reflux with ethanolic potassium cyanide then the product obtained is:
a. Ethyne
b. Ethane nitrile
c. Propene
d. Propane nitrile
47. The order of reactivity of alkyl halides towards elimination reaction is
a. 3o > 2o > 1o
b. 1o > 2o > 3o
c. 3o > 1o > 2o
d. 2o > 1o >3o
48. The reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is
a. R-I > R- Br > R-CI > R -F
b. R-F > R –CI > R – Br > R-I
c. R-F > R-I > R – Br > R – CI
d. R-I > R – CI > R – Br > R – F
49. Identify Z in the following series:
![]()
a. Br(CH2)2Br
b. Br(CH2)2CN
c. CN(CH2)2CN
d. BrCH = CHCN
50. Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by SN2 mechanism because of:
a. Steric hindrance
b. Insolubility
c. Instability
d. Inductive effect
