Chemistry Chapter 3 Entry Test MCQs
26. If P, V, T represent pressure, volume and temperature of the gas, the correct representation of Boyle’s law is
a. V 1/P (at constant T)
b. V 1/T (at constant P)
c. PV = nRT
d. PV = RT
27. At constant temperature, in a given mass of an ideal gas:
a. Pressure always remains constant
b. The ratio of pressure and volume always remains constant
c. The product of pressure and volume always remains constant
d. Volume always remains constant
28. If 20 cm3 gas at 1 atm is expanded to 50 cm3 at constant T, then what is the final pressure:
a. 1 x 1/20 x50
b. 20 x 1/50
c. 50 x 10/20
d. 50 x 1/20
29. Which of the following graphs represent Boyle’s law:
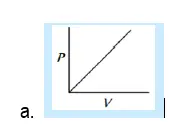
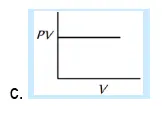
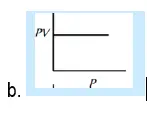
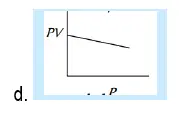
30. At constant pressure, the volume of fixed mass of an ideal gas is directly proportional to
a. Degree Fahrenheit
b. Absolute temperature
c. Any one
d. Degree centigrade
31. Pressure remaining the same, the volume of a given mass of an ideal gas increases for every degree centigrade rise in temperature by definite fraction of its volume at
a. 0K
b. 0oC
c. 0oF
d. 25oC
32. Correct gas equation is
a. P1T2/V1 = P2V2/T2
b. V1T2/P1 = V2T1/P2
c. V1V2/T1T2 = P1V2
d. P1V1/P2V2 = T1/T2
33. “Equal volumes of all gases at the same temperature and pressure contain equal number of particles.” This statement is a direct consequence of:
a. Ideal gas equation
b. Avogadro’s law
c. Boyle’s Law
d. Charle’s law
34. A gas is enclosed in a container of 20cm3 volume with a moving piston. What will be the effect of increasing T from 20oC to 100oC, on the freely moving molecules of gas?
a. T has no effect on freely moving gas
b. Colliding capability of molecules will decrease
c. Volume will be increased
d. Pressure will become half
35. The volume of a gas at 00C is 273 cm3. What would be the volume of gas at 150 0C at constant pressure.
a. 523 cm3
b. 400 cm3
c. 323 cm3
d. 423 cm3
36. Volume occupied by a gas at one atmospheric pressure and 0oC is V mL. Its volume at 273 K will be
a. 2V
b. V ml
c. 2ml
d. V/2 ml
37. For a given mass with initial volume ‘v’, if pressure is reduced to one half and absolute temperature is increased two times. The volume will become
a. 4V
b. 2V2
c. 6V
d. V/4
38. There are equal number of oxygen and hydrogen molecules with 740mm Hg of total pressure in a closed vessel. If oxygen is removed from the system, then pressure
a. becomes double of 740 mm Hg
b. becomes half of 740mm Hg
c. remains the same
d. becomes 1/9th of the total pressure
39. The correct order of rate of diffusion is
a. SO2 > NO2 > CO2 > CO
b. CO2 > CO > NO2 > SO2
c. CO> NO2 > CO2 > SO2
d. CO > CO2 > NO2 > SO2
40. Two equal mass of different gases have same temperature and pressure can have
a. Same moles
b. Same volume
c. Same no. of molecules
d. All of these
General Gas Equation + KMT
41. In the ideal gas equation PV = nRT, the value of R depends upon
a. Temperature of gas
b. Units of measurement
c. Nature of gas
d. Pressure of gas
42. All of the following are conclusions of the kinetic theory of gases except
a. Relation of average kinetic energy of gases to temperature
b. Derivation of the Van der waal’s equation
c. Graham`s law of diffusion
d. Derivation of Boyle’s and Charle’s law
43. If the temperature of a gas is increased four times, then its average K.E.
a. Decreases 2 times
b. Increases 2 times
c. Decreases 4 times
d. Increases 4 times
44. 2gm of O2 at 27 oC and 760mm of Hg pressure has volume:
a. 11.2 lit
b. 1.5 lit
c. 22.4 lit
d. 2.8 lit
45. According to kinetic theory of gases
a. Molecules have considerable volume
b. There are intermolecular attractions
c. The velocity of molecules decreases after each collision
d. No intermolecular attractions
46. Root means square velocity shows the highest value for__________ at STP
a. Cl2
b. CO
c. He
d. O2
47. PV=nRT, according to this equation, if concentration of a gas increases the pressure will
a. increase
b. lower
c. remain same
d. Double
48. The units of ‘R’ depends upon
a. Pressure and volume
b. Moles
c. Temperature
d. All of these
49. Which equation is correct to calculate the relative molecular mass of gas
a. M = mPR / VT
b. M = mPRT/V
c. M = mRT / PV
d. M = PV / MRt
50. The kinetic molecular theory assumes that gas particles:
a. Have no mass
b. Occupy a fixed position in space
c. Are attracted to each other
d. Are in constant random motion
