Physics Chapter 10 Entry test MCQs
Topic 10
Electronics
1. The applied input a.c. power to a half-wave rectifier is 100 watts. The d.c. output power obtained is 40 watts. What is the rectification efficiency?
a. 40%
b. 50%
c. 95%
d. 80%
2. The ripple factor indicates the number of ripples in the
a. A.C input
b. D.C output
c. A.C output
d. None of these
3. For a half wave or full wave rectifier the Peak Inverse Voltage of the rectifier is always
a. Equal to the input voltage
b. Greater than the input voltage
c. Greater than the input voltage for full wave rectifier and smaller for the half wave rectifier
d. Smaller than the input voltage
4. The device which coverts A.C into D.C is called
a. Rectifier
b. Oscillator
c. Diode
d. Transducer
5. The types of rectifications are
a. 5
b. 3
c. 2
d. 4
6. Rectification is possible by
a. Amplifier
b. Transistor
c. Capacitor
d. Diode
7. The semiconductor diode can be used as a rectifier because———-.
a. It has high resistance to the current flow when reverse biased
b. It has low resistance to the current flow when forward biased & high resistance when reverse biased
c. Its conductivity increases with rise of temperature
d. It has low resistance to the current flow when forward biased
8. In the half wave rectifier circuit shown. which one of the following wave forms is true for diode, the output across C and D?
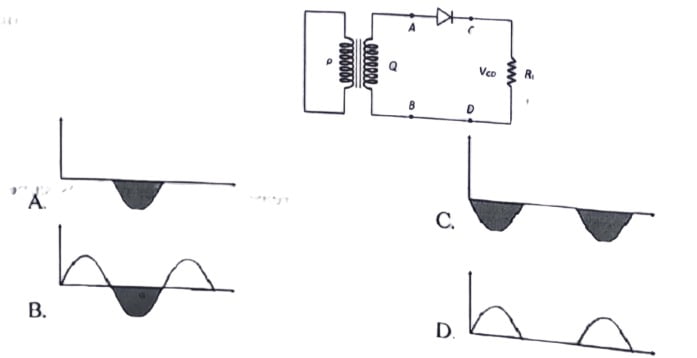
9. For the given circuit of PN-Junction diode, which of the following statement is correct?
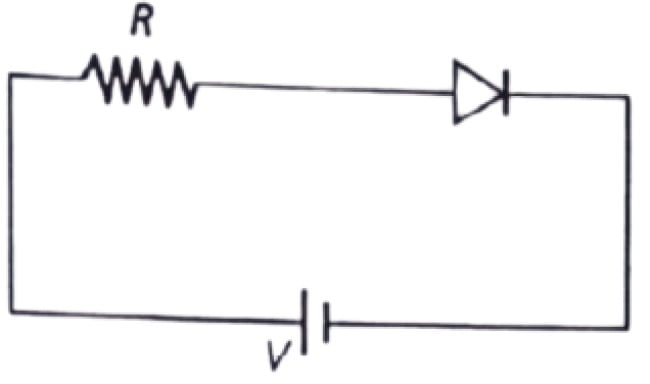
a. in forward biasing the voltage across R is 2V
b. in reverse biasing the voltage across R is V
c. in forward biasing the voltage across R is V
d. in reverse biasing the voltage across R is 2V
10. The simplest type of rectification known as half wave rectification is obtained by———-.
a. Suppressing the harmonics in A.C voltage
b. Using a transistor
c. Using a Coolidge tube
d. Suppressing half wave of A.C supply by using diode
11. Output of half wave rectifier is suitable only
a. For running a D.C motor
b. Charging batteries
c. To operate radio
d. All of these
12. During the interval 0→T/2 the forward biased diode offers
a. Very small current flow through it
b. Very small resistance
c. Zero resistance
d. Very high resistance
13. In a half wave rectifier, the frequency of the input is N, the frequency and form of the output will be
a. N and Pulsating
b. N/2 and Pulsating
c. N and continuous
d. 2 N and steady
14. The most common device used as filter is
a. Resistor
b. Capacitor
c. Transistor
d. Transformer
15. The method by which only one half of A.C cycle is converted into direct current is called
a. Half wave rectification.
b. Half wave amplification
c. Full wave amplification
d. Full wave rectification
16. If time period of input T in the full wave bridge rectifier circuit, then time period of the pulsating output of the circuit will be
a. 2T
b. T
c. T/4
d. T/2
17. In a bridge rectifier how, many diodes conduct during each half cycle of input A.C
a. 3
b. 2
c. 1
d. All
18. If a full wave rectifier circuit is operating from 50 Hz mains, the fundamental frequency in the ripple will be
a. 100 Hz
b. 50 Hz
c. 25 Hz
d. 70.7 Hz
19. In figure the input is across the terminals A and C and the output is across B and ID. Then the output is
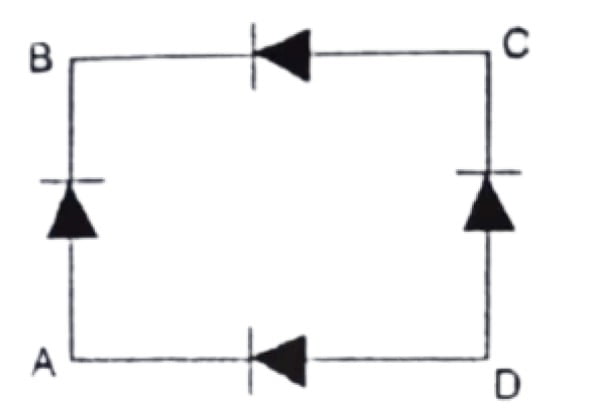
a. Half wave rectified
b. full wave rectified
c. Zero
d. Same as input
20. To reduce ripples in the output of bridge rectifier we should use
a. Diodes having high forward resistance
b. Diodes having low forward resistance
c. A filter circuit
d. Low frequency A.C
21. In full wave rectification, the output D.C. voltage across the load is obtained for—————.
a. The negative half cycle of input A.C
b. The complete cycle of input A.C
c. The positive half cycle of input A.C
d. All of the above
22. In the following picture
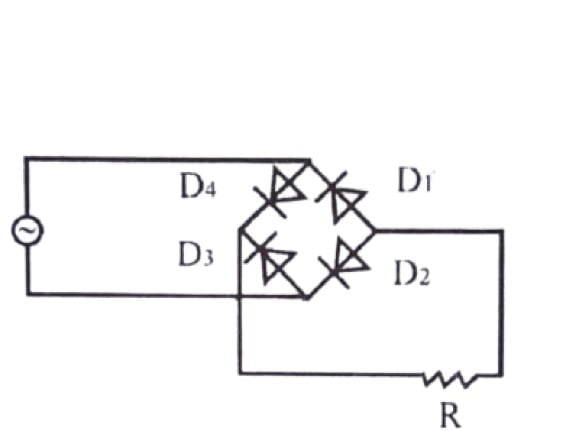
a. D1 and D3 conducts simultaneously
b. D1 and D2 conducts Alternatively
c. D1 and D2 conducts simultaneously
d. Both A and C
23. Output voltage of rectifier is not smooth. as: It can be made smooth by using a circuit known
a. Bridge circuit
b. Wheat stone circuit
c. Filter circuit
d. Ripple circuit
24. In the diagram, diodes are arranged alternating voltage must be applied for the full wave rectification where input
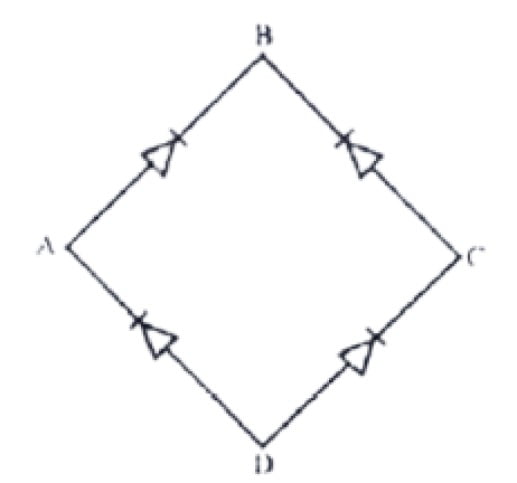
a. Across A and B
b. Across B and D
c. Across A and C
d. Across B and C
25. The basic reason why a full wave rectifier has a twice the efficiency of a half wave rectifier is that
a. Its ripple factor is much less
b. It make use of transformer
c. Its output frequency is double the frequency
d. It utilizes both half cycle of the input
