Physics Chapter 11 Entry test MCQs
Topic 11
Dawn of Modern Physics
1. Threshold wavelength for a metal having work function Wo is X. What is the threshold wavelength for the metal having work function 2W0?
a. λ / 2
b. 4λ
c. λ / 4
d. 2λ
2. An electric bulb of 100 W converts 3% of electrical energy into light energy. If the wavelength of light emitted is 6625 Å, the number of photons emitted in 1 s is———— ( h = 6.625 x 10-34 J.sec)
a. 1021
b. 1017
c. 1015
d. 1019
3. The wavelength of a photon needed to remove a proton from a nucleus which is bound to the nucleus with 1 MeV energy is nearly
a. 1.2 x 10-6 nm
b. 1.2 nm
c. 1.2 x 101 nm
d. 1.2 x10-3 nm
4. If K.E. of free electron is doubled, its de Broglie wavelength become
a. 1/√8
b. √2
c. 1/√2
d. 2
5. In a photon-particle collision, the quantity that does not remain conserved is
a. Number of photons
b. Total energy
c. Total momentum
d. None of these
6. The momentum of a photon is 2 x 10-16 gm-cm/sec. Its energy is
a. 6 x 10-6 erg
b. 0.61 x 10-26 erg
c. 6 x 10-8 erg
d. 2 x 10-26 erg
7. Ratio of momentum of photons having wavelength 4000 angstrom and 8000 angstroms is
a. 20:1
b. 2:1
c. 1:20
d. 1:2
8. A radio station emits 10 kW power of 90.8 MHz. Find the number of photons emitted per second
a. 1.6 x 1030
b. 1.6 x 1028
c. 1.6 x 1032
d. 1.6 x 1029
9. The energy of a photon is 3 x 10-19 J. Its momentum
a. 10 ^ – 11 kgms-1
b. 10 ^ – 27 kgms-1
c. 3 x 10 ^ – 7 kgms-1
d. 9 x10 ^ – 11 kgms-1
10. The mass of a photon at rest is
a. 1.67 x10-35 kg
b. 1 a.m.u.
c. Zero
d. 9 x10-31 kg
11. The momentum of a photon is p. The frequency associated with it is given by
a. ph/c
b. pc/h
c. h/pc
d. hc/p
12. Photon A has twice the energy of photon B. What is the ratio of the momentum of A to that of B?
a. 1:1
b. 2:1
c. 1:2
d. None of these
13. The value and units of the Plank’s constant ‘h’ can be expressed as:
a. 6.63 x 10-43Js
b. 6.63 x 10-34 Js-1
c. 3.63 x 10-34 Js
d. 6.63 x 1-34 Js
14. Let nr and nb respectively the number of photons emitted by a red bulb and a blue bulb of equal power in a given time.
a. nr > nb
b. nr = nb
c. information is insufficient to get a relation between nr and nb
d. nr < nb
15. λ is proportional to
a. 1/E for both photons and particles
b. 1/√E for both photons and particles
c. 1/E for photons and 1/√E particles
d. 1/√E for photons and 1/E particles
16. which of the following graphs correctly represents the variation of the particle momentum with associated with de-Broglie wavelength?
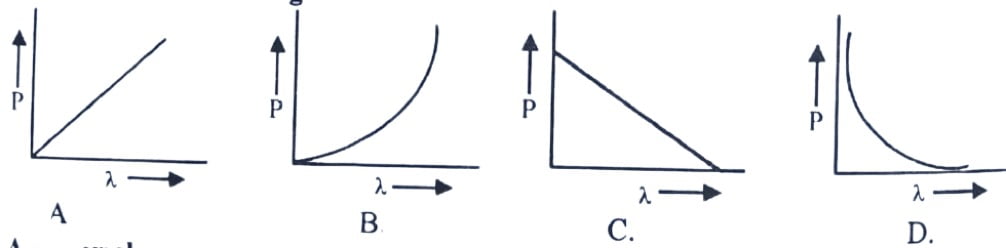
17. A material particle with a rest mass mo is moving with speed of light c. The associated de-Broglie wavelength is given by
a. 0
b. h/moc
c. ∞
d. moc/h
18. A photon is considered to have:
a. Momentum
b. Energy
c. Wavelength and frequency
d. All of these
19. If electron and proton have same De-Broglie wavelength, which have greater speed
a. Electron
b. Proton
c. Both have same
d. Electron and Proton can’t have wavelength
20. The wavelength of a moving particle is inversely proportional to
a. Energy
b. Mass
c. Momentum
d. Velocity
21. According on De-Broglie, an electron can be regarded as:
a. Are negligible
b. Particle and wave both
c. Particle only
d. None of these
22. Davidson determine the wavelength of scattered electron from the relation:
a. λ= h/2mVe
b. λ= 2h/√mVe
c. λ= h/2√2mVe
d. λ= h/√2mVe
23. If an electron in accelerated through a potential of 54 volts, its de-Broglie wavelength will be:
a. 1.66 x 10-9 m
b. 1.66 x 10-8 m
c. 1.66 x 10-17m
d. 1.66 x 10-10 m
24. In Davisson and Germer experiment, target crystal is made up of
a. Aluminium
b. Copper
c. Silver
d. Nickle
25. A body of mass speed of 5 m/hr. So de-Broglie wavelength related to it is of the order (h = 6.26 x 10-34 Js)
a. 10-30 m
b. 10-10 m
c. 10-40 m
d. 10-20 m
