Physics Chapter 5 Entry test MCQs
Topic 5
Thermodynamics
1. Heat was given to a body, which raises its temperature by 1°C is————.
a. Thermal capacity
b. Water equivalent
c. Specific heat
d. Temperature gradient
2. The thermal capacity of 40g of aluminium (specific heat = 0.2cal° g-1 C-1 ) is—————.
a. 200cal°C-1
b. 40cal°C-1
c. 8cal°C-1
d. 160cal°C-1
3. 80g of water at 30°C is poured on a large block of ice which is at 0°C. The mass of ice that melts is—————-.
a. 150g
b. 30g
c. 1600g
d. 80g
4. Mud houses are cooler in summer and warmer in winter because—————-.
a. Mud is a bad conductor of heat
b. Mud is a good conductor of heat
c. Mud can adapt according to temperature
d. Mud is a superconductor of heat
5. Heat capacity of a substance is infinite. It means————-.
a. No change in temperature
b. Heat is given out
c. Heat is first given out and then taken out
d. Heat is taken out
6. The change in internal energy, when a gas is cooled from 927° to 27° is?
a. 200%
b. 100%
c. 75%
d. 300%
7. Two cylinders of equal size are filled with equal amount of ideal diatomic gas at room temperature. Both the cylinders are fitted with pistons. In cylinder A the piston is free to move, while in cylinder B the piston is fixed. When same amount of heat is added to cylinder A raises by 20 K. What will be the rise temperature of gas in cylinder B
a. 15K
b. 28K
c. 10K
d. 20K
8. The relation for the 1st law of thermodynamics can be expressed as:
a. ∆Q = ∆U
b. ∆Q = ∆W
c. ∆Q = (∆U)/(∆W)
d. ∆Q = ∆U + ∆W
9. Examples of first law of thermodynamics are
a. Human metabolism
b. Working of bicycle pump
c. Brakes applied by an automobile
d. All of these
10. 1st law of thermodynamics is consequence of conservation of
a. Energy
b. Work
c. Heat
d. All of these
11. Which statement about the first law of thermodynamics is correct?
a. The increase in the internal energy of system equal the heating of the system plus the workdone by the system
b. The heating of a system equal to the increase of its internal energy plus the work done on the system
c. The work done on a system equals the increase of its thermal energy plus the heating of the system
d. The increase in the internal energy of a system equal the heating of the system minus thework done by the system
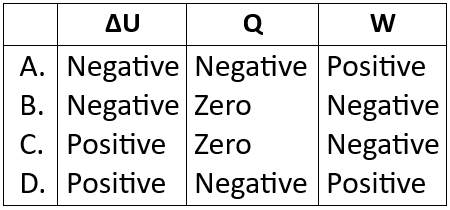
12. The first law of thermodynamics may be expressed as shown ΔU=Q+W
Where ΔU is change in internal energy, Q is the heating of the system, W is the work done on the system. A fixed mass of ideal gas at high pressure contained in balloon. The balloon suddenly bursts, causing the gas to expand and cool. In this situation, which row describes the values of ΔU, Q and W?
13. In a thermodynamic system working substance is an ideal gas, its internal energy is in the form of
a. Kinetic and potential energy
b. Kinetic energy only
c. Potential energy
d. None of these
14. In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
a. K.E and P.E both
b. Only K.E
c. Only gravitational energy
d. Only P.E
15. Which one is true for internal energy?
a. It is a state function of a system
b. It is sum of all forms of molecular energies of a system
c. All are correct
d. It is proportional to transnational K.E of the molecules
16. If two system X and Y are in thermal equilibrium. If X is heated at constant volume and Y is heated at constant pressure, and again finally maintained at thermal equilibrium, then heat Q given to the systems X and Y and internal energy U stored in the systems X and Y are
a. Qx < QY and Ux < Uy
b. Qx = Qy and Ux = Uy
c. Qx < QY and Ux = Uy
d. Qx < QY and Ux < Uy
17. The internal energy of a body is maximum when its temperature is
a. .-273 K
b. 0 K
c. – 273°C
d. 273 K
18. An ideal gas is pressed at a constant temperature. Its internal energy
a. Increases
b. Decreases
c. Remains the same
d. First increases and then decreases
19. When 20 J of work was done on a gas, 40J of heat energy was released. If the initial internal energy of the gas was 70J, what is the final internal energy?
a. 60J
b. 50J
c. 110J
d. 90J
20. A system goes from A to B via two processes I and II as shown in figure. If ∆U1 and ∆U2 are the changes in internal energies in the processes I and II respectively, then
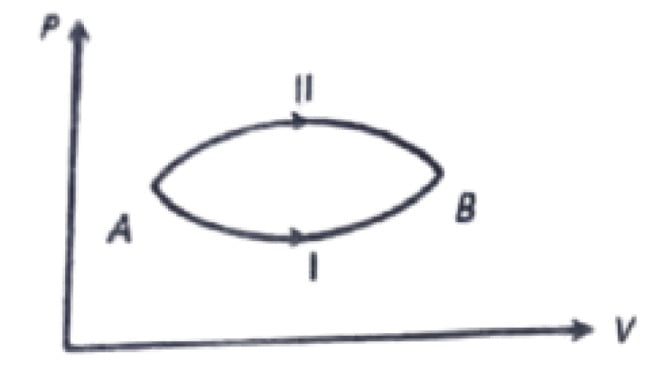
a. ∆UII > ∆UI
b. ∆UI = ∆UII
c. ∆UII < ∆UI
d. Relation between ∆UI and ∆UII can not be determined
21. By rubbing the objects together, their internal energy:
a. Decreases
b. Increases
c. Becomes zero
d. Remains constant
22. The internal energy of an ideal gas depends upon only:
a. Temperature
b. Pressure
c. Volume
d. All of these
23. If a system undergoes contraction of volume, then the work done by the system will be
a. Negligible
b. Zero
c. Positive
d. Negative
24. The work done in the isochoric process is
a. Variable
b. Constant
c. Depends on situation
d. Zero
25. A gas undergoes the cycle of pressure and volume changes W→X→Y→Z→W shown in the diagram.
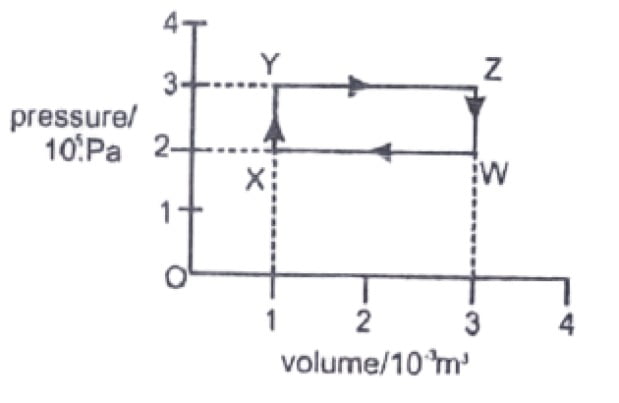
what is the network done by the gas?
a. -600J
b. 0J
c. 200J
d. -200J
