Physics Chapter 5 Entry test MCQs
26. Calculate the heat absorbed by the system in going through the process as shown in the figure?
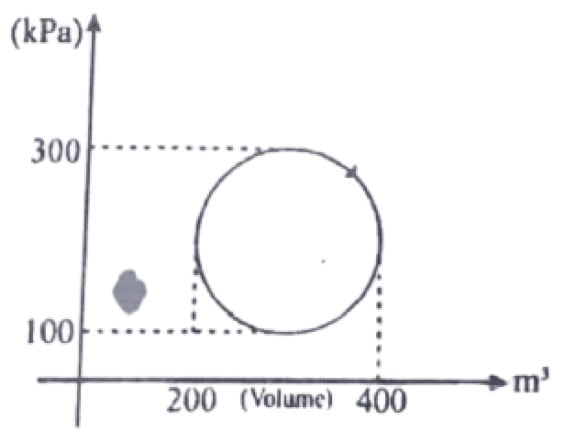
a. 31.4J
b. 31.4×106J
c. 3.14J
d. None
27. Work done by air when it expands from 50 litres to 150 litres at a constant pressure of 2 atmospheres is
a. 2 x 100 joules
b. 2 x 104 joules
c. 2×10-5 ×100 joules
d. 2×105 x100 joules
28. A system is taken from State A to B through three different Paths 1,2 and 3. The work done is maximum in.
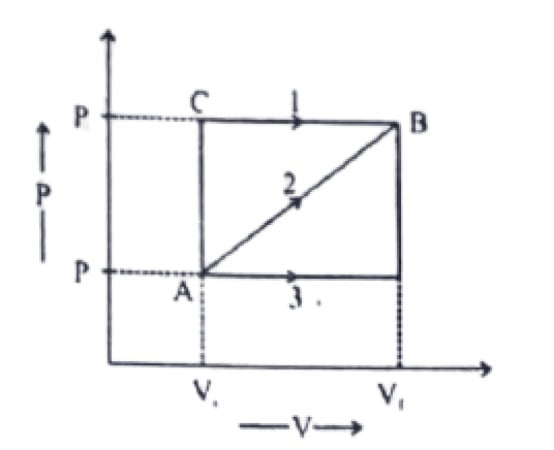
a. Process 3
b. Process 2
c. Process 1
d. equal in all processes
29. What is the total work performed on the gas as its transformed from state a to state c, along the path indicated.
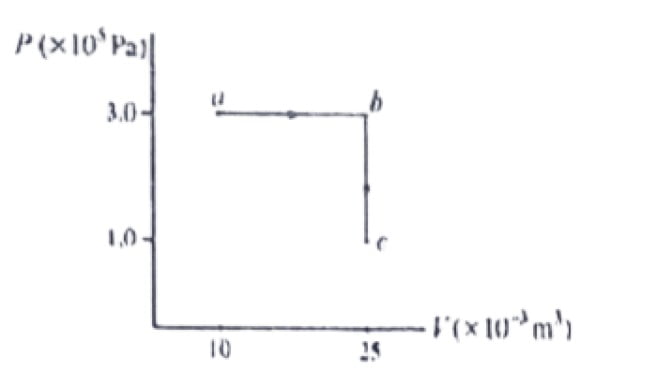
a. 1500J
b. 4500J
c. 3000J
d. 5000J
30. An ideal Gas is Taken around ABCA as shown in the above P-V diagram. The work done during a cycle is
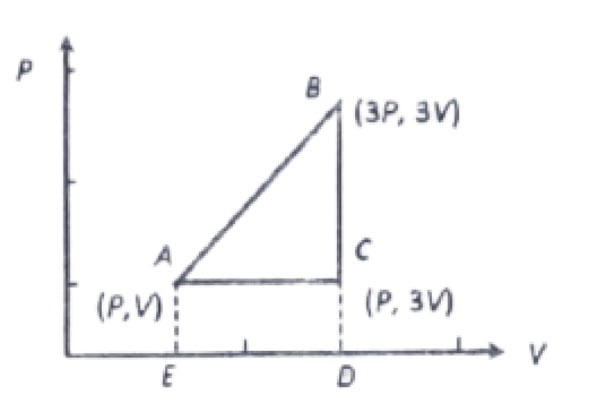
a. 2PV
b. 1/2PV
c. PV
d. Zero
31. The equation WP(V2-V1) represent work done by a gas in
a. An adiabatic expansion
b. Free expansion
c. An expansion at constant pressure
d. An isothermal expansion
32. Find the change in internal energy of the system when a system absorbs 2 kilocalorie of heat and at the same time does 500 joules of work
a. 7900 J
b. 8200 J
c. 6400 J
d. 5600 J
33. In the following indicator diagram, the net amount of work done will be
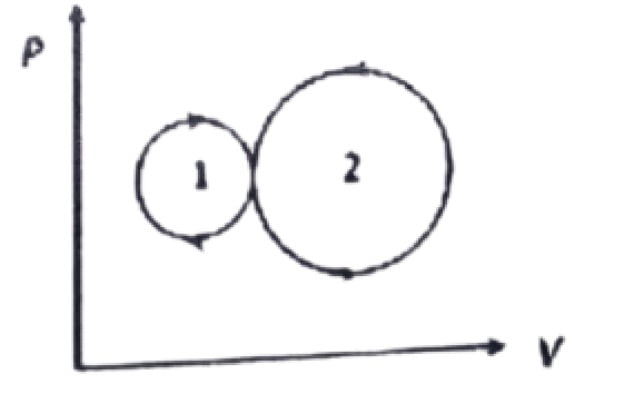
a. Zero
b. Positive
c. Infinity
d. Negative
34. A system is described in terms of thermodynamics variables
a. Volume (V)
b. Pressure (P)
c. Temperature (T)
d. All of these
35. The concent of temperature is related to
a. First law of thermodynamics
b. Zeroth law of thermodynamics
c. Third law of thermodynamics
d. Second law of thermodynamics
36. Which of the following statement is correct for any thermodynamic system?
a. Internal energy and entropy are state functions
b. The internal energy changes in all processes
c. The work done in an adiabatic process is always zero
d. The change in entropy can never be zero
37. Thermodynamic is the study of relationship between
a. Heat & Liquid
b. Heat & Surrounding
c. Heat & chemical energy
d. Heat & other form of energy
38. In the figure curves AB and CD represent the relation between pressure P and volume V of an ideal gas. One of the curves represents an isothermal expansion and the other represents an adiabatic expansion. Which curve represents an adiabatic expansion?
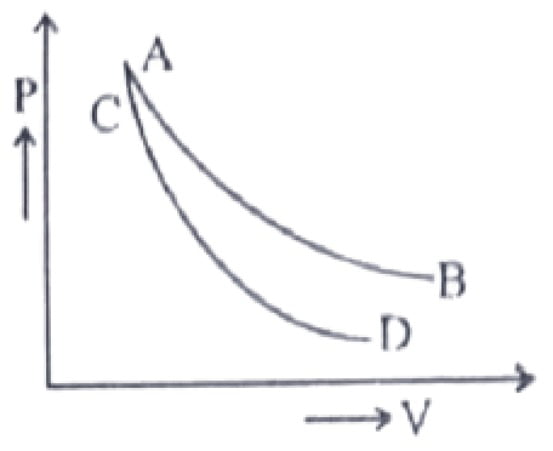
a. Curve AB
b. Curve CD
c. Both “A” and “B”
d. None of these
39. Heat added at constant volume of a gas is used to
a. To do external work
b. To increase its internal energy
c. Either “A” or “C”
d. Both “A” and “C”
40. When heat is given to a gas in an isobaric process then
a. The work is done by the gas
b. Internal energy of the gas increases
c. Both ‘A’ and ‘B’
d. None of these
41. If the volume of a gas is deceased by 10% during isothermal process than its pressure will
a. Increase by 10%
b. Decrease by 10%
c. Increase by 11.11%
d. Decrease by 11.11%
42. During which process the volume of system remains constant
a. Isobaric
b. Isothermal
c. Adiabatic
d. Isochoric
43. In pressure-volume diagram given below, the isochoric, isothermal, and isobaric parts respectively, are
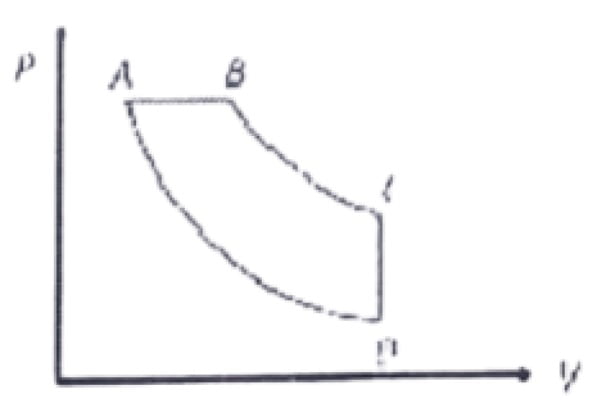
a. CD, DA, AB
b. AB, BC, CD
c. BA, AD, DC
d. DC, CB, BA
44. A gas does 10J of external work in adiabatic process while expanding, then the change in internal energy is:
a. 20 J
b. 10J
c. 0 J
d. -10 J
45. A fixed mass of an ideal gas undergoes the changes represented by X→Y→Z→X As shown below.
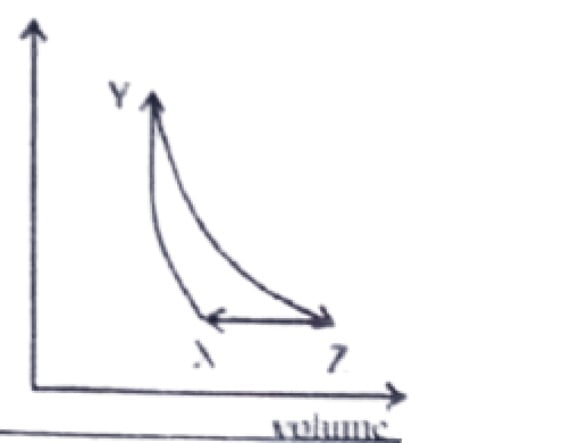

46. During the adiabatic expansion of 2 moles of a gas, the internal energy of the gas is found to decrease by 2 joules, the work done during the process on the gas will be equal to
a. -2J
b. 2J
c. -1J
d. 1J
47. Starting with the same initial conditions, an ideal gas expands from volume v1 to V2 three different ways. The work done by the gas is W1, if the process is purely isothermal. W2 if purely isobaric and W3 if purely adiabatic then
a. W2>W3>W1
b. W2>W1>W3
c. W1>W3>W2
d. W1>W2>W3
PAST PAPER MCQS
48. What is the factor upon which change in internal energy of an ideal gas depends?
a. Changed in volume and temperature
b. Change in volume
c. Path followed to change internal energy
d. Change in temperature
49. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1kg of substance through 1 K is called;
a. Specific heat
b. Heat capacity
c. One calorie
d. 1 Joule
50. If one mole of an ideal gas is heated at constant pressure, then the first law of thermodynamics can be written as:
a. Cv∆T = Cp∆T + P∆T
b. Cp∆T = Cv∆T + P∆V
c. ∆CvT = ∆CvT + P∆V
d. Cp∆T = Cv∆T + V∆P
51. If Cv= 5/2 R, Cp will be
a. 2/7 R
b. 5/5 R
c. 7/2 R
d. 5/2 R
52. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 10 moles of water from 70k to 80K (molar heat capacity of water 75.24J) is:
a. 95.243
b. 0.75243
c. 572.4J
d. 75243
53. The sum of all forms of molecular energies (kinetic and potential) of a substance termed as?
a. Elastic energy
b. Internal energy
c. Absolute energy
d. Heat energy
54. In which process the entire of heat supplied to the gas is converted to the internal entry of the gas?
a. Isothermal process
b. Isochoric process
c. Adiabatic process
d. Isobaric process
55. The internal energy of a system during an isothermal process:
a. Become zero
b. Decreases
c. Remain constant
d. Increases
56. In a certain process, 400J of heat energy is supplied to a system and at the same tin 150J of work is done by the system. The increase in internal energy of system is
a. 250J
b. 150J
c. 500J
d. 300J
57. The rapid escape of air from a burst tyre is an example of:
a. Isothermal
b. Isothermal
c. Isochoric
d. Adiabatic
58. Cp-Cv value, find if 3moles of gas is gives
a. 5R
b. 3R
c. 7R
d. 2R
