Physics Chapter 7 Entry test MCQs
26. If a wire conductor of 0.2 ohm resistance is doubled in length, its resistance becomes
a. 0.6 ohm
b. 0.4 ohm
c. 1.0 ohm
d. 0.8 ohm
27. r = 0 R = ∞ (V = epsilon – Ir) then
a. V<epsilon
b. V>epsilon
c. V = 0
d. V = epsilon
28. An 8Ω resistance connected to a battery with internal resistance draws 1.6 A and if a 30Ω resistance is connected to the same battery if draws 0.5 (A. What is the current drawn by a 6Ω resistance from this battery
a. 2.2 A
b. 2A
c. 2.5 A
d. None of these
29. Internal resistance of ideal current source is
a. Zero
b. Infinite
c. Very high
d. Very low
30. Internal resistance is the resistance offered by———–.
a. Conductor
b. Source of e.m.f
c. Capacitor
d. Resistor
31. An electric current source is actually source of
a. Charge
b. Current
c. Power
d. Energy
32. A new flashlight cell of emf 1.5 volts gives a current of 15 A, when connected directly to an ammeter of resistance 0.042. The internal resistance of cell is
a. 0.06Ω
b. 0.04 Ω
c. 10Ω
d. 0.10Ω
33. If the current in electric bulb decreases by 0.5%, then the power in the bulb decreases by approximately
a. 2%
b. 1%
c. 0.25%
d. 0.5%
34. What will be energy used by the battery if the battery has to drive 6.2810 18 electrons with potential difference of 20 V across the terminal?
a. 10 joules
b. 5 joules
c. 20 joules
d. 15 joules
35. 1 horse power=
a. 746mW
b. 746 kW
c. 746MW
d. 746 W
36. If R1 and R2 are respectively the filament resistances of a 200-watt bulb and 100-watt bulb designed to operate on the same voltage, then
a. R₂ is two times R1
b. R1 is two times R2
c. R1 is four times R2
d. R2 is four times R1
37. Two electric bulbs, one of 200 volt 40 watt in a house wiring circuit and the other 200 volt 100 watt are connected
a. The resistance of the filament in 40-watt bulb is more than the resistance in 100-watt bulb
b. They have equal currents through them
c. The resistance of the filament in 100-watt bulb is more than the resistance in 40-watt bulb
d. The resistance of the filaments in both the bulbs is same
38. A heater coil is cut into two equal parts and only one part is now used in the heater. The heat generated will now be
a. one-fourth
b. halved
c. doubled
d. four times
39. A battery is used to light a 24 watt electric pump. The battery provides a charge of 120C in 60sec.
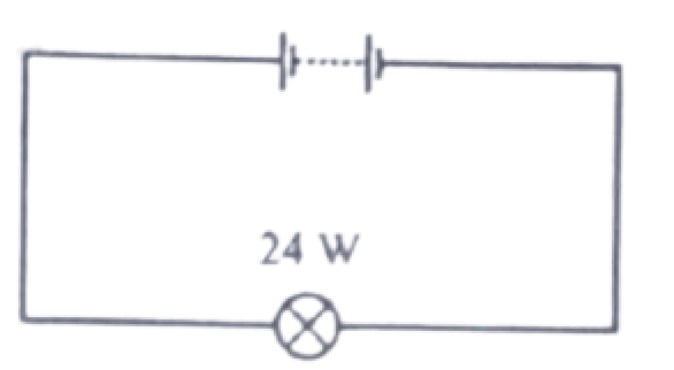
What is the potential difference across the bulb?
a. 5V
b. 12V
c. 24V
d. 120V
40. A 100 W, 200V bulb is connected to a 160 V supply. The actual power consumption would be
a. 72 W
b. 64 W
c. 90 W
d. 100 W
41. Electrical energy is converted to heat at the rate of——–.
a. l2R
b. IRt
c. Vlt
d. l2Rt
42. A 40 W lamp turns half the electrical energy to give light. How much light energy does it give out in 10 s?
a. 400 J
b. 200 J
c. 40 J
d. 800 J
43. An electrical bulb marked 100 W, 200 V would mean the resistance is———.
a. 400 ohm
b. 200-ohm
c. 50 ohm
d. 50 ohm
44. You are given four bulbs of 25 W, 40 W, 50 W and 60 W. Which bulb has the lowest resistance?
a. 50 W
b. 25 W
c. 40 W
d. 60 W
45. SI unit of resistivity is
a. Ω -m
b. Ω – m2
c. (Ω – m)-1
d. (Ω – m)-1
46. The following four wires are made temperature. Which one of them has of the same material and are at the same highest electrical resistance
a. length=200 cm, diameter = 2 mm
b. length= 100 cm, diameter = 1mm
c. length = 300 cm, diameter =3 mm
d. length= 50 cm, diameter= 0.5 mm
Past paper mcqs
47. A wire has resistance 100 Ohm at 0° C and 200 Ohm at 100° C What is its temperature coefficient in K-1
a. – 1/273
b. -0.01
c. 1/273
d. 0.01
48. The produced by a current I in the wire of resistance R during time interval t is
a. I2 Rt
b. l2 / R t
c. I R2 t
d. l2 / R / t
49. The fractional change in resistance per Kelvin is known as:
a. Thermal coefficient.
b. Temperature coefficient of resistance
c. Volumetric coefficient of expansion
d. Linear coefficient of expansion
50. The energy supplied by the cell to the charge carriers is derived from the conversion of:
a. Chemical energy into Electrical energy
b. Heat energy into Electrical energy
c. Mechanical energy into Electrical energy
d. Solar energy into Electrical energy
